7th Pay Commission Table Matrix | 7th Pay Commission Table Matrix PDF | 7th CPC Chart |7th Pay Commission Table Matrix Report Summary
The Government of India established the Pay Commission in 1947 to make recommendations on improvements to the salary structure of its employees. Seven Pay Commissions have been established on a regular basis since India’s independence to assess and offer suggestions on the work and pay structure of all civil and military divisions of the Indian government. The article contains useful about the 7th Pay Commission.

The government has altered the pension restrictions for both teaching and non-teaching workers at both central and state universities in response to the seventh pay commission’s recommendations. A total of 25,000 central universities, deemed university, and University Grants Commission (UGC)-maintained university retirees will benefit from the government’s decision.
Table of Contents
7th Pay Commission – Latest Update
- The Centre has increased the Dearness Allowance by 17% to 28%, which will benefit approximately 1.1 crore central government employees and retirees. This came into news on Wednesday 14th July 2021.
- Bihar CM Nitish Kumar has stated that madrassa professors in the state will receive 7th pay commission remuneration, which will help thousands of academicians.
- Because the raise takes effect retroactively on January 1, employees will be paid in arrears for the month of January.
- Dearness Allowances will henceforth be paid at a rate of 28% to central government employees and retirees.
- The ministry will raise the retirement age for constables to commandants (senior superintendents of police) to 60 years from the current 57 years in order to bring retirement age uniformity.
- The Ministry of Railways has also decided to form a committee to consider the addition of new categories to the Risk and Hardship Allowance program. The committee’s principal task would be to “review holistically the addition of new categories within the ambit of the Risk and Hardship Allowance introduced by the 7th CPC.”
Impact of HRA Structure on Inflation – 7th Pay Commission
According to a study report published by the RBI’s monetary policy section. At its height, the rise in in-house rental allowance for central government employees recommended by the 7th central pay commission increased CPI inflation by about 35 basis points. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a mechanism for calculating the weighted average of prices for a variety of consumer products and services, including food, transportation, and medical care. It is calculated by averaging the price changes for each item in a given range of items.
New Benefit for Railway Employees
Railway personnel can now apply for Leave Travel Concession (LTC) for the first time. Government employees and their spouses who work for the Indian Railways are not eligible for LTC because they have access to a “Free Pass” program.
Will Central Government Staff Get Revised Allowance under 7th Pay Commission?
Starting in July 2018, the government will begin disbursing revised allowances to nearly 4.9 million central government employees in accordance with the Seventh Pay Commission. HRA, outstation detention allowance, accidental allowance, trip allowance, and ghat allowance will all be included in the new allowance.
The Lavasa committee was tasked with looking into the 7th Pay Commission’s recommendation to eliminate 53 of the 196 allowances and incorporate another 36 into existing ones. On 14 of these allowances, the Lavasa committee is seeking responses from the ministries of defense, railways, and posts.
Will Central Government Employees Receive Revised Allowances from July 2018 under the 7th Pay Commission?
Employees at the central level now have a 25% raise in basic pay, although their HRA has been reduced significantly. The Ashok Lavasa Committee examined the 7th Pay Commission’s recommendations, particularly those concerning allowances, and presented its results to the finance minister.
7th Pay Commission Recommendations
Recommendations of the 7th Pay Commission are listed below:
- Pay Matrix: Once the 7th Pay Commission is implemented, a government employee’s salary will be determined by the level in the new Pay Matrix rather than the former system of Grade Pay.
- Minimum pay for government employees:The entry-level payment for a new government recruit is now Rs. 18,000 per month. The minimum monthly remuneration for a newly recruited Class I Officer is now Rs.56, 100.
- Maximum pay for government employees:The 7th Pay Commission recommends that government employees’ maximum pay be increased to Rs.2.5 lakhs for apex grade employees such as Cabinet Secretaries and those on the same scale.
- The 7th Pay Commission recommended a new pay structure that included all existing levels in the pay matrix and did not create any new levels or hierarchies.
Summary of 7th Pay Commission
Read below to know the brief Summary of the 7th Pay Commission:
- The 7th pay commission will create a new pay matrix and pay scale that would provide pensioners and government employees a 2.57 percent raise on their current salaries, and a central government employee will be paid twice as much as before.
- According to the 2018 Budget, apex government jobs such as cabinet secretary will have a pay range of Rs.2.5 lakh.
- The new basic pay threshold for entry-level government employees would begin at Rs.18, 000, up from the previous threshold of Rs.7, 000.
- The new “Fitment factor” established by the 7th Pay Commission will be a 3% annual increase for all employees.
- Furthermore, if a 50 percent dearness allowance is introduced, House Rent Allowance (HRA) would grow to 27 percent, 18 percent, and 9 percent, respectively.
- The Pay Matrix is a Central Government employee’s status in a certain office, and it will be utilized in place of the previous grade pay standard going forward.
- The pay matrix for defence and other forces employees/ personnel start at a minimum payable rate of Rs. 21,700 and go up to a maximum of Rs. 2, 50,000. The finance minister has selected and developed this arrangement.
- The maximum earnings and remuneration for government employees have been increased as a result of the 7th Pay Commission’s new recommendations. The Apex grade personnel would be paid an enhanced salary of Rs.2.25 lakh per month, with the maximum remuneration for Cabinet officers being Rs.2.5 lakh.
- Shifts and adjustments in the government compensation structure’s pay scales and matrices will have an impact on the country’s financial situation. The Indian government will be responsible for the whole expense of this initiative. The Union Budget of 2018 made out Rs.73, 650 crore for this purpose, with the Railway sector bearing a cost of Rs.29, 300 crore on top of that.
Steps to Calculate 7th Pay Commission
You can use one of many 7th Pay Commission calculators to calculate your salary in the new structure, which indicates that you should figure your total salary/pay package as follows:
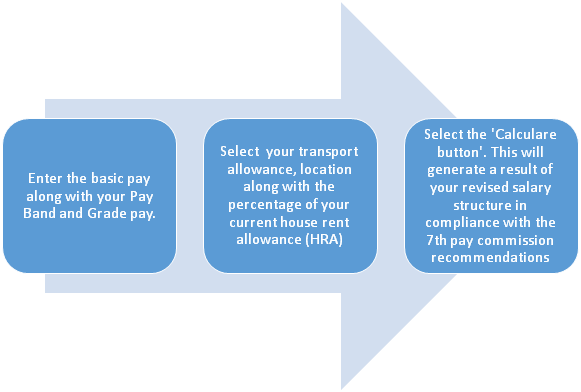
If a government employee’s monthly basic wage is 20,000 rupees, his or her monthly basic pay will be 51,400 rupees (20,000 x 2.57). The allowances, such as DA, TA, and medical reimbursement, will be calculated after that. The gross monthly salary of an employee is determined by the person’s basic monthly pay and total allowance.
The amendments made by the 7th Pay Commission will take effect in August 2018. With the implementation of the 7th Pay Commission, a new era will begin. All altered salaries, remunerations, and allowances will be effective beginning with the preceding month’s salary (July), which will be paid in August.
There is still no clarity on whether employee arrears will be released in one lump sum or in installments. Considering managing a core group of central government employees. These employees’ pay has been increased by the government since 2016. Considering the rate of inflation, employees thought that the compensation increase was insufficient to cover rising living costs, and therefore urged that the government alter the salary structure under the 7th pay commission. Employees in the government feel that aid is on the way and that it will arrive soon.
7th CPC Pay Matrix
| Existing Pay Brands | Existing level of Grade pay | Available for* | New levels |
| PB-1 | 1800 | C | 1 |
| 1900 | C | 2 | |
| 2000 | C,D | 3 | |
| 2400 | C | 4 | |
| 2800 | C,D | 5 | |
| PB-2 | 3400 | D | 5A |
| 4200 | C,D | 6 | |
| 4600 | C,D | 7 | |
| 4800 | C,D | 8 | |
| 5400 | C | 9 | |
| PB-3 | 5400 | C,D,M | 10 |
| 5700 | M | 10A | |
| 6100 | D | 10B | |
| 6100 | M | 10B | |
| 6600 | C,D,M | 11 | |
| 7600 | C | 12 | |
| PB-4 | 7600 | M | 12 |
| 8000 | D | 12A | |
| 8400 | M | 12B | |
| 8700 | C | 13 | |
| 8700 | D | 13 | |
| 8900 | C | 13A | |
| 8900 | D | 13A | |
| 9000 | M | 13B | |
| 10000 | 14 | ||
| HAG | 15 | ||
| HAG+ | 16 | ||
| Apex | 17 | ||
| Cabinet Secretary, Defence Chiefs | 18 | ||
| *C: Civil, D: Defence, M: Military Nursing Service (MNS) |
The new 7th Pay Commission Pay Matrix has taken into account all of the above criteria. The grade pay has been considered, and the levels have been reorganized. Employees in the federal government can now look up their current salary level and assess their current position as well as their potential for advancement over the course of their careers. Procedures for calculating the 7th CPC are also made easier.
Approaches Followed by the Panel on the 7th Pay Commission
According to the panel, a holistic approach was used in determining the levels of salaries, allowances, and other perks of the pay structure. In addition to other research, the panel commissioned three studies from expert bodies:
a) IIM Ahmedabad conducted a study to determine the nature and amount of total pay for selected government employment profiles compared to similarly located profiles in CPSUs and the private sector.
b) An investigation by the Institute of Defence Studies and Analyses into the nature, scope, and components of defense spending and pensions;
c) A study by IIM Kolkata on the fiscal consequences of the V and VI CPC on the Union and State Governments’ finances.
According to the panel report, the new pay system for civilians and armed services personnel has been put out generally as an open-ended, tiered matrix. It has been kept in mind that a person should not stagnate but should have a fair chance to advance via merit and earn greater emoluments in order to avoid frustration.
The goal was to connect merit with a fair wage. While compensation increases may not be able to keep up with market pressures, it was ensured that the pay structure is not so unattractive that the best talent is not drawn to government jobs.