Trade Credit Meaning | Trade Credit Formula | How Trade Credit Works | What are the benefits of trade credit
Trade Credit is a method of ordering and getting goods or services for business purposes without paying the providers in cash right away. It is a form of inter-firm trade credit between buyers and sellers, in which items are sent or services are provided in advance of payment. Credit conditions will change from one company to the next and from one industry to the next. Payment-on-delivery companies, such as online shopping sites, may have a shorter credit period than an industrial manufacturer. Projects are spread out over a longer length of time in this situation, and payments may be made regularly based on the completion of pre-determined time slots. Read below to check the detailed information related to Trade Credit like Features, Benefits, Formula, Credit Period, and much more.
Table of Contents
About Trade Credit
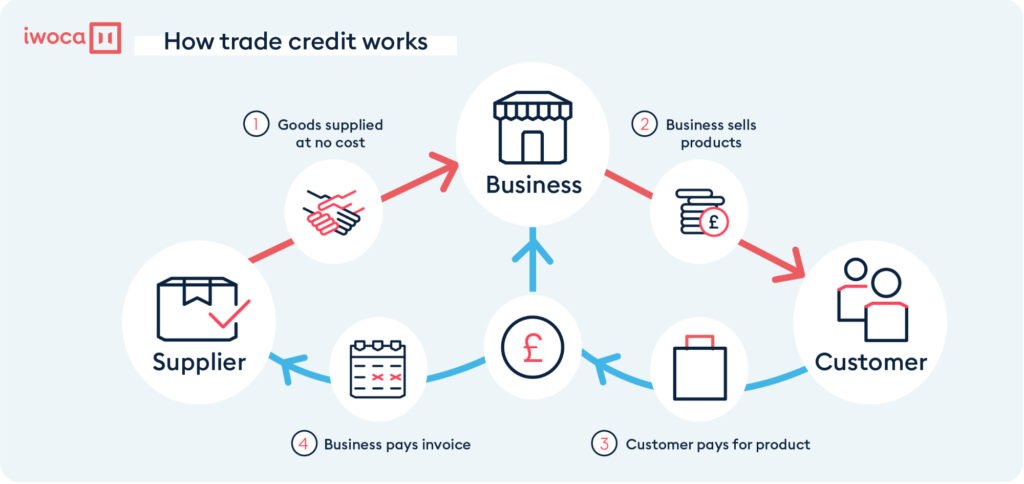
Trade credit is a business-to-business relationship in which the borrower (buyer) is given a credit limit by the supplier, allowing the borrower to buy now and pay later. When a businessman receives the equipment, machinery, materials, or other business-related things and does not pay cash immediately, but rather later on or before the due date, trade credit is used. The credit limit is determined by the buyer’s creditworthiness, company requirements, present assets and obligations, repayment capability, and creditworthiness. When favorable terms are agreed upon with a business’s supplier, trade credit can be a useful tool for developing firms. This method efficiently reduces the impact on cash flow compared to immediate payment. This sort of financing aids in the reduction and management of a company’s capital requirements.
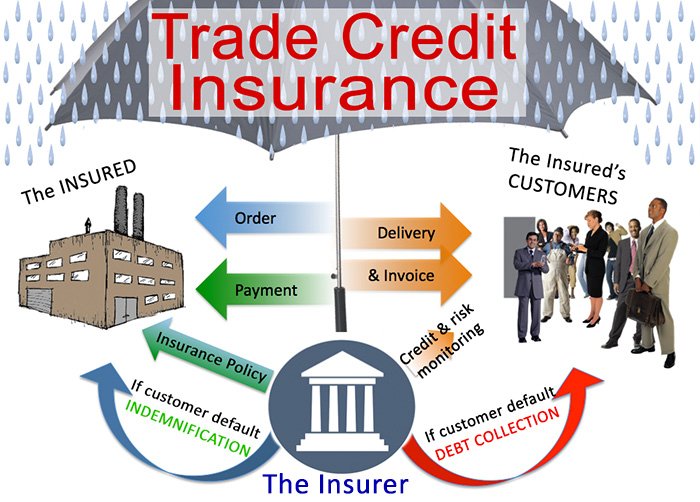
Trade Credit Trade-Offs
From the standpoint of the borrower, credit can permit growth or development that might otherwise be impossible if the company had to pay for things right away. One key disadvantage is that interest payments can quickly accrue and overwhelm borrowers (resulting in significant obligations which may compound). Credit allows the borrower to be more convenient (leading to more transaction activity) while also providing the lender with recurrent interest income. Providing credit to a borrower carries the risk of default, as the borrower may be unable to meet his or her debt obligations.
Benefits of Trade Credit
Some of the key benefits of the Trade Credit are as follows:
- As long as the prerequisites are met, maintaining an agreement is pretty simple
- An agreement can be simple to put together
- A type of working capital financing that could be low-cost
- Most firms can utilize it for deliveries of goods or services, and they are protected by late payment laws
Disadvantages of Trade Credit
Some of the disadvantages of the Trade Credit are as follows:
- Failure to adhere to the terms could result in the loss of a supplier who provides a cash flow advantage rather than additional financing
- Loss of the early payment discount is a possibility
- Some firms, such as internet shops, are unable to use it.
- Customers may pay late, thus there are no promises.
- Your clients may request advantageous trade credit terms, reducing any cash flow benefit.
Features of Trade Credit
Some of the key features of the Trade Credit are as follows:
- Buyer and seller come to an arrangement internally.
- Serves as a source of working capital
- Financing that is available right away and for a limited period
- The company’s financial and repayment history are used to determine to fund.
- If payment is made within the discount period, there will be no interest to pay.
- Increases cash flow and lowers capital expenditures
Trade credit formula
The formula for Trade Credit is given below:
Amount to pay = Total Amount x (1-discount)
Credit Period
Credit terms differ depending on the industry. A jewelry store, for example, might sell diamond engagement rings for 5/30, net 4 months. Net 7 may be used by a food distributor selling fresh fruits and vegetables. In general, while determining a credit period, a company must consider three factors:
- The likelihood of the consumer failing to pay: If a company’s customers are in high-risk industries, it may be forced to give severe credit terms
- Perishability of the items: If the collateral values of the goods are poor and cannot be sustained for lengthy periods, the credit will be limited.
- The size of the account: A tiny account will have a shorter credit duration. Managing small accounts is more expensive.
Policy on Cash Discounts
Trade credit is denoted by three numerals, the first two of which represent the discount % and time, and the third number denotes the ultimate due date. For example 3/10 Net 30.
What does 3/10 Net 30 indicate?
The trade-credit offered is 3/10 Net 30, and if 3/10 is displayed, it means that the borrower will receive a 3% discount if the balance is paid within 10 days of the date of receipt. Alternatively, the borrower must pay the entire amount within 30 days after the date of issuance.
For example, if a person buys Rs. 10 lakh from Company A on 3/10 net 30 terms and pays within 10 days, the borrower only has to pay (Rs. 1000000 – Rs. 30000 = Rs. 970000). If the consumer pays after 10 days, however, he must pay the entire amount of Rs. 10 lakh.
Banks that provide Trade Credit
Some of the banks that provide Trade Credit are as follows:
- HDFC bank
- Bank of Baroda
- United Bank of India
- DCB Bank
Instruments of Trade Credit
The majority of credit is granted based on an open account. This means that the invoice, which is issued with the shipping of goods and signed by the buyer as proof of receipt, is the only formal credit instrument used. The firm and its clients then record the transaction in their accounting books. The firm may occasionally ask the customer to sign a promissory note or IOU. This is utilized when the order is significant and the company expects a potential collection issue. Promissory notes can help you avoid issues later on when it comes to the presence of a credit agreement. One issue with promissory notes is that they are only signed after the products have been delivered.
A commercial draught is one approach to get a credit commitment from a customer before the goods are delivered. A commercial draught is often written by the selling firm, requiring the customer to pay a set amount by a specific date. The draught, along with the shipping invoices, is subsequently transmitted to the customer’s bank. Before handing over the bills, the bank will require the buyer to sign the draught. After that, the products can be delivered to the buyer.
A sight draught is used when rapid payment is necessary. Before the products can be transported, monies must be transferred to the bank. Even a signed draught is often insufficient for the vendor. The seller may mandate that the lender pay for the products and collect the money from the buyer in this situation. The paper is known as a banker’s acceptance when the banker agrees to do so in writing. That is, the banker assumes payment obligation.
Credit Analysis
A company tries to differentiate between customers who will pay and consumers who will not pay while issuing credit. Creditworthiness can be determined using a variety of sources, including the following:
- Banks: In most cases, banks will assist their business customers in obtaining information on the creditworthiness of other companies.
- Credit reports from other companies on a customer’s payment history: Many businesses sell data on a company’s creditworthiness.
- Financial statements: A company can request financial statements from a customer. It is possible to utilize rules of thumb based on estimated financial ratios.
- The firm’s payment history with the consumer: The most obvious technique to predict a customer’s likelihood of non-payment is to look at whether he or she has paid past invoices with the creditor.
Credit’s Five C’s:
- Character: The customer’s willingness to pay back debts.
- Capital: The customer’s financial reserves are referred to as capital
- Capacity: The ability of a customer to meet credit obligations using operating cash flows.
- Conditions: The state of the economy as a whole.
- Collateral: In the event of a default, collateral is a pledged asset.
FAQ’s
Banks that provide Trade Credit options are as follows:
• United Bank of India
• HDFC bank
• Bank of Baroda
• DCB Bank
The trade-credit offered is 3/10 Net 30, which means that if the 3/10 symbol is shown the borrower will receive a 3% reduction if the amount is paid within 10 days of receipt. Alternatively, the borrower must pay the full amount within 30 days of the issuance date.