ECGC Scheme Share Price | Function of ECGC Scheme | How Does ECGC Scheme Work | ECGC Full Form in Export |
The Export Credit Guarantee Corporation of India (ECGC) is a government-owned company in India that is run by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry. The ECGC, which is entirely owned by the Indian government, was founded in 1957 with the goal of increasing exports by providing credit risk insurance and other services to exporters. ECGC Scheme is also started by the Export Credit Guarantee Corporation of India.

Table of Contents
What is ECGC Scheme?
India’s Export Credit Guarantee Corporation (ECGC) provides export credit insurance. In ECGC Scheme, the insurance product assures the exporter that the amount owed from the overseas customer will be received. Hence, export credit insurance is designed to safeguard an exporter’s receivables in India. In the event that the customer or the foreign bank is unable to pay the assured value due to commercial, political, or other reasons, the insurance pays a portion of the assured value.
Export Credit Guarantee Corporation Limited (ECGC) is an open-ended credit insurance policy that is a legal necessity. The ECGC Policy was established by the Indian government in 1957 to encourage commerce by providing credit risk insurance and related services to exporters. The Ministry of Commerce regulates the Export Credit Guarantee Scheme (ECGC), which is governed by a board of directors that includes representatives from the RBI, the government, and the banking, export, and insurance industries.
Benefits of ECGC Scheme
The benefits of export credit insurance, and why it’s a necessity for anyone shipping goods internationally is explained below:
- The export credit insurance policy covers export risk and insurance.
- You won’t have to worry about sales money being recovered on time if you have a credit insurance policy in place. Credit insurance frees up time that would otherwise be spent managing and assessing credit risk, allowing you to focus on business development and growth.
- It also allows you to be flexible with your credit duration and/or credit line, allowing you to increase them as needed. Giving new and existing customers additional credit flexibility will encourage them to conduct business with you and buy more from you. As a result, export credit can assist you in increasing your sales.
How does ECGC Scheme work?
Export credit insurance is crucial for a variety of reasons as an exporter. The following is a simplified representation of how the process works:
- Credit insurance might also increase your chances of obtaining export financing. If a lender is certain that your invoices are covered by credit insurance, obtaining financing for your export firm becomes easier due to reduced risk.
- You can also explore new markets with confidence thanks to the protection given by credit insurance. Credit insurance can frequently cover up to 95% of your invoice, allowing you to take more risks and enter new markets without fear of losing money.
- Export credit insurance businesses also provide other services such as debt and client counselling, as well as debt collection assistance.
Advantages & Disadvantages of ECGC Scheme
The advantages and disadvantages of ECGC are mentioned in the table below:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Protect Accounts | Not available for high-risk accounts |
| Expand to new markets | Possibility of default and bad faith |
| Security of Cashflow | It does not cover non-payment situations |
| Tax Benefits | Limits certain actions |
| Minimize bad debts |
Function of ECGC Scheme
The Export-Import Bank of India (ECGC), a government-owned company formed to encourage export and import in India, offers exporters a variety of credit risk insurance products to protect them against losses in the export of commodities. The distribution of ECGC credit plans would be facilitated by South Indian Bank, which has over 400 branches throughout 14 states. The major ECGC functions are diverse, yet they all fall under the umbrella of export credit risk management.
- Its main function is to provide a variety of risk insurance products that cover export losses and bad debts.
- The ECGC also provides banks and financial institutions with export credit insurance coverage so that they can provide trade-risk coverage to exporters.
- The Corporation also provides overseas investment insurance in the form of equity or loans to Indian enterprises undertaking international joint ventures.
- The ECGC policy also provides exporters with guidelines on export-related operations, such as credit rating-based information on various nations.
- The ECGC cover can also assist exporters with obtaining export financing from banks and financial organizations (i.e. Bank Export Credit).
- Finally, it aids exporters in debt collection and creditworthiness checks of foreign consumers.
- In addition, there is no GST on insurance premiums.
Cost of Export Credit Insurance
Export credit insurance premiums are often computed as a proportion of total invoices/accounts receivable. This may vary depending on the circumstances of the transaction and the country in which one operates.

Benefits of ECGC’s Export Credit Insurance for Indian Exporters
Under the credit risk domain, the ECGC Policy offers a variety of services. The following are some of the most important ECGC products and services offered to Indian exporters as a result of the ECGC Policy
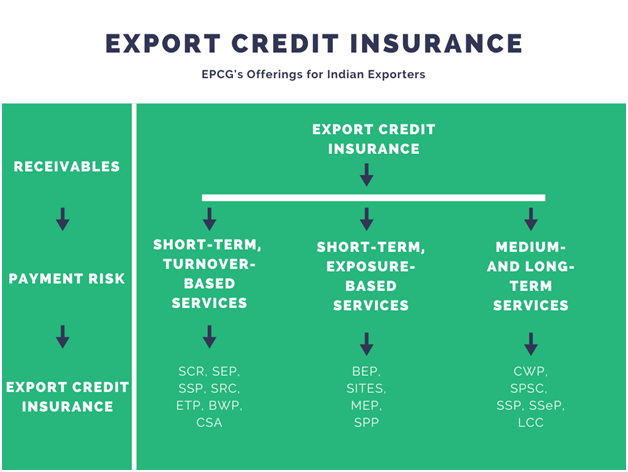
Short-Term Turnover-Based Services
These are the sorts of payment arrangements available to Indian exporters in the short-term (turnover-based) period:
- SCR (Shipments Comprehensive Risks) Plan: It is a 12-month insurance policy accessible to exporters with a turnover of more than Rs. 500 crores.
- Small Exporters Policy (SEP): SEP is for exporters with a revenue of less than Rs. 5 crore and a maximum risk coverage of less than Rs. 2 crores.
- SSP (Specific Shipment Policy):SSP covers shipments made within the policy term for up to 80% of the total value of the shipment.
- Service Policy (SRC): The Service Policy (SRC) is for single, long-term service contracts. It is appropriate for Indian enterprises that undertake to supply technical or professional services to international principals.
- ETP (Export Turnover Policy):ETP is for large exporters who pay a premium of at least Rs. 20 lakhs per year.
- BWP (Exports (Specific Buyers) Policy): BWP provides the same protection against shipments addressed to a specific customer as SCRP, ETP, and other policies.
- Consignment Exports Policy (Stockholding Agent) (CSA): CSA covers consignment export shipments sent by the exporter to their foreign agents.
Short-Term Exposure-Based Services
These are the payment arrangements for exports in the short-term (exposure-based) period:
- Buyer Exposure Policy (BEP):BEP opposes a large number of shipments made to a single buyer with a streamlined method and reduced premium.
- Policy on IT-Enabled Services Single Customer (SITES): SITES is offered for billings for IT services given to a single customer.
- Micro Exporter Policy (MEP):MEP is a 90 percent coverage exposure policy for exporters with a turnover of less than Rs. 100 lakh.
- Software Project Policy (SPP): The Software Project Policy (SPP) is for exporters of software and related services who will be paid in foreign currency.
Medium- and Long-Term Services
For medium and long-term services, these are the preferred modes of export payments:
- Construction Works Policy (CWP): The CWP is created for an Indian contractor working on a civil construction project in another country.
- SPSC (Specific Policy for Supply Contract):SPSC is for exporters who have a credit period of less than 180 days and want to keep their shipments insured.
- Specific Shipment Policy (SSP):SSP, like its namesake policy for short-term shipments, is for exporters who have agreed to supply capital goods to foreign purchasers on deferred payment terms.
- Specific Services Policy (SSeP): The SSeP is intended to cover payment risk arising from a variety of overseas service contracts, such as technical requirements, professional hiring, leasing, and so on.
- LCC (Letter of Credit Confirmation): An LCC covers Indian banks from foreign bank default on credit lines.
Aside from the aforementioned services, the ECGC also offers MSMEs export factoring, insurance coverage for buyer’s credit and line of credit, customer-specific covers, overseas investment insurance, and the establishment of a national export insurance account to help with medium- and long-term exports. It also provides exporters’ banks with a comprehensive range of credit risk insurance solutions.
Sign up for ECGC Scheme
To sign up for ECGC Scheme, follow the below steps:
- First of all go to the ECGC website i.e https://www.ecgcltd.in/ecgcportal/SignUp.jsp
- A home page will appear as shown below:

- On the home page, you need to select correct user type either Exporter or Bank.
- After that you need to enter:
- Either User ID or
- IFSC Code (for bank type users) or
- IE Code (for exporter type users)
- Next you need to set a password.
- Type the correct captcha code.
- Then click on submit option.
- The registered Email Id will receive a link to authenticate the credentials.
- If you have any questions or need to update your registered email address, please contact your local branch.
Letter of Credit vs. Export Credit Insurance
Both of these methods aid in lowering payment risk and ensuring timely payment. A Letter of Credit is taken by the buyer and issued on his behalf by the buyer’s bank. Furthermore, any trade conducted under a letter of credit requires the buyer’s consent. A letter of credit is the ideal alternative for every new commercial transaction.
Export credit insurance, on the other hand, is used to protect and secure accounts receivable in overseas trade operations. In addition, the insurance will cover the cost of any default payments or even bankruptcy. This insurance is purchased by the supplier, and the buyer’s permission is not necessary.
Pro Tips
- Always save enough in your ECGC account to cover your shipments for the next month/quarter because ECGC premium is a guaranteed practitioner’s guidance for export payment.
- Because EPCG premiums are exempt from GST, you should make sure that your policy’s maximum liability is sufficient to cover all of your existing debts at any one moment.
- Use the ECGC database to run a background check on your potential purchasers and see whether any exporters or the ECGC have ever had a bad experience with them.
Warnings
- A delay in filing claims, like any other insurance product, can result in your credit insurance claim being denied.
- Make no fresh shipments to a delinquent buyer without the ECGC’s permission.
- At least once a month, notify the ECGC about bills that are past due for more than 60 days.